Vermi Bed & Azolla Bed
Vermi Bed
This is a specially designed, controlled environment where earthworms are raised to decompose organic waste into nutrient-rich compost, also known as vermicompost. It is a highly efficient system for organic waste management, improving soil fertility, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. This is an essential tool for both small-scale gardeners and large-scale farms aiming to enhance soil health, reduce waste, and create a sustainable ecosystem.
A vermi bed is an efficient, low-maintenance solution for recycling organic waste, improving soil health, and producing high-quality compost. By harnessing the natural decomposing power of earthworms, this is not only reduces waste but also promotes a sustainable, eco-friendly approach to farming and gardening. Whether you are a hobby gardener or a commercial farmer, investing in a vermi bed is an excellent step toward promoting soil fertility, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing plant growth.

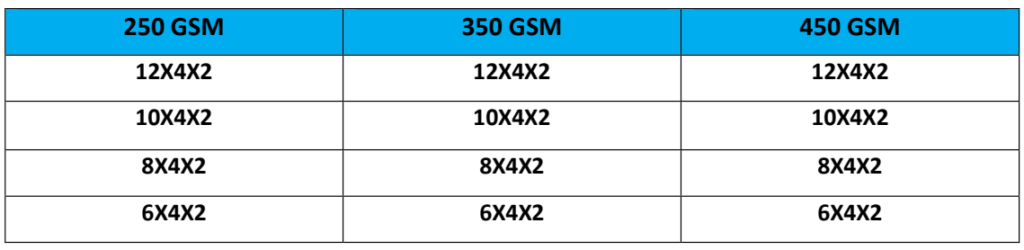
Dimensions
Azolla Bed
This is a carefully constructed, controlled environment where Azolla, a small floating aquatic fern, is grown for various agricultural, environmental, and aquaculture purposes. This is a highly productive, nitrogen-fixing plant that thrives in waterlogged conditions and offers a range of ecological benefits, including improving soil fertility, boosting crop yields, and enhancing aquatic ecosystems. It is also known for its role in biological nitrogen fixation, making it an essential tool for sustainable agriculture and organic farming.
This is a system designed to grow Azolla plants under controlled conditions, typically in shallow water. It consists of a water-based platform, often built in ponds, tanks, or small rectangular beds, that provides the ideal habitat for Azolla to grow and multiply rapidly. These beds are designed to hold Azolla plants in place while ensuring they receive adequate nutrients, sunlight, and moisture.

Dimensions

Vermi & Azolla Bed
Both play a vital role in organic farming and sustainable agriculture. They are specialized setups designed to foster the growth of essential organisms (earthworms for vermi beds and Azolla for Azolla beds) that provide numerous benefits, such as enhancing soil fertility, promoting nitrogen fixation, and improving soil health.
1. Vermi Bed (Vermiculture Bed)
A vermi bed is a specially designed area or container used to cultivate earthworms for the process of vermicomposting. This process involves earthworms breaking down organic waste into nutrient-rich vermicompost or worm castings, which can then be used as an organic fertilizer to improve soil health.
Benefits of Vermi Beds:
- Rich Organic Fertilizer: The vermicompost produced in vermi beds is rich in essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and micronutrients. These nutrients are readily available to plants, promoting faster and healthier growth.
- Improved Soil Structure: Vermicompost improves the soil’s texture, enhancing its water retention, drainage, and aeration. It also increases the microbial diversity in the soil, which helps break down organic matter more efficiently.
- Pest Control: The process of vermiculture helps in the breakdown of pest-infested organic material, reducing the prevalence of harmful pests in the soil.
- Waste Recycling: Vermiculture helps recycle organic waste, reducing landfill waste while providing an environmentally friendly way to enrich the soil.
- Enhanced Plant Growth: The addition of vermicompost directly to the soil promotes vigorous plant growth, better flowering, and fruiting.
Vermi & Azolla Beds: A Detailed Overview
Both vermi beds and Azolla beds play a vital role in organic farming and sustainable agriculture. They are specialized setups designed to foster the growth of essential organisms (earthworms for vermi beds and Azolla for Azolla beds) that provide numerous benefits, such as enhancing soil fertility, promoting nitrogen fixation, and improving soil health. Here’s a comprehensive explanation of these beds, their setup, functions, and applications:
1. Vermi Bed (Vermiculture Bed)
A vermi bed is a specially designed area or container used to cultivate earthworms for the process of vermicomposting. This process involves earthworms breaking down organic waste into nutrient-rich vermicompost or worm castings, which can then be used as an organic fertilizer to improve soil health.
Vermi Bed Setup:
- Material: Vermi beds are typically made of wood, plastic, or concrete, designed to maintain adequate moisture levels and provide aeration for the worms. They can be large rectangular beds or compact trays, depending on the scale of the operation.
- Dimensions: The size of the vermi bed can vary. For a small-scale setup, a bed measuring 1 meter by 1 meter can be used. Larger systems may have beds ranging from 2 meters by 4 meters or even bigger. The depth of the bed usually varies from 15 to 30 cm.
- Bedding: The bed is filled with a bedding material that retains moisture and provides a habitat for the worms. Common bedding materials include:
- Coconut coir
- Compost
- Farmyard manure
- Shredded paper
- Leaf litter
- Sawdust Bedding should be moist but not waterlogged to create a favorable environment for the worms.
Earthworm Species Used:
- Eisenia foetida (Red Wiggler): The most common species for vermiculture. These worms are highly efficient in breaking down organic waste.
- Eisenia hortensis (European Nightcrawler): Another popular species, known for its ability to work in larger composting systems.
- Eudrilus eugeniae: This species is commonly used in tropical and subtropical areas due to its fast reproduction rate and composting ability.
Vermiculture Process (Vermicomposting):
- Organic Waste Addition: Organic waste (such as vegetable scraps, manure, and food residues) is added to the vermi bed. The earthworms consume this waste, breaking it down into nutrient-rich worm castings.
- Worm Care: Earthworms require a moist, cool environment (preferably between 15°C to 25°C) to thrive. The bed should be kept covered to prevent temperature fluctuations, excess moisture loss, or pest infestation.
- Harvesting Vermicompost: After about 2-3 months, the bed will be filled with rich, dark, crumbly vermicompost. The castings are then harvested by moving the worms and the compost to one side of the bed, allowing the new material to be collected on the other side.
Benefits of Vermi Beds:
- Rich Organic Fertilizer: The vermicompost produced in vermi beds is rich in essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and micronutrients. These nutrients are readily available to plants, promoting faster and healthier growth.
- Improved Soil Structure: Vermicompost improves the soil’s texture, enhancing its water retention, drainage, and aeration. It also increases the microbial diversity in the soil, which helps break down organic matter more efficiently.
- Pest Control: The process of vermiculture helps in the breakdown of pest-infested organic material, reducing the prevalence of harmful pests in the soil.
- Waste Recycling: Vermiculture helps recycle organic waste, reducing landfill waste while providing an environmentally friendly way to enrich the soil.
- Enhanced Plant Growth: The addition of vermicompost directly to the soil promotes vigorous plant growth, better flowering, and fruiting.
Applications:
- Home Gardens: Vermi beds are ideal for small-scale home gardening, providing high-quality organic fertilizer for vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants.
- Agriculture: Farmers use vermi beds to generate large quantities of compost for agricultural fields, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
- Landscaping: Vermicompost is often used in landscaping projects to enhance soil fertility and improve plant health.
2. Azolla Bed
An Azolla bed is a system used to cultivate Azolla, a fast-growing aquatic fern that plays a significant role in natural nitrogen fixation. Azolla is often used in rice paddies, as it can fix atmospheric nitrogen into the soil, providing a natural, sustainable source of nitrogen for crops.
Benefits of Azolla Beds:
- Natural Nitrogen Fixation: Azolla is a well-known biofertilizer that can fix nitrogen from the air into the soil. It works symbiotically with the cyanobacterium Anabaena, which captures nitrogen and makes it available to the plants, reducing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers.
- Soil Enrichment: When harvested and incorporated into the soil, Azolla adds organic matter and nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, improving soil fertility.
- Improved Crop Yield: The addition of Azolla to crops like rice and vegetables can lead to increased yields, especially in nitrogen-deficient soils.
- Water Conservation: Azolla helps in reducing water evaporation from fields by providing a natural cover over the water, thereby preserving moisture.
- Pest Control: Azolla also helps in controlling the growth of harmful algae and weed species in aquatic environments, making it an excellent plant for integrated pest management.
Vermi beds and Azolla beds are integral components of sustainable farming and organic agriculture. Vermiculture (through vermi beds) focuses on recycling organic waste into nutrient-rich compost, while Azolla cultivation (through Azolla beds) offers a unique solution for nitrogen fixation and soil enrichment. Both practices contribute to the creation of healthy, fertile soils and reduce dependency on chemical fertilizers, promoting environmentally friendly agricultural practices. These beds provide an efficient and low-cost method for improving soil quality, increasing crop yields, and enhancing environmental sustainability, making them vital tools for modern organic farming.
